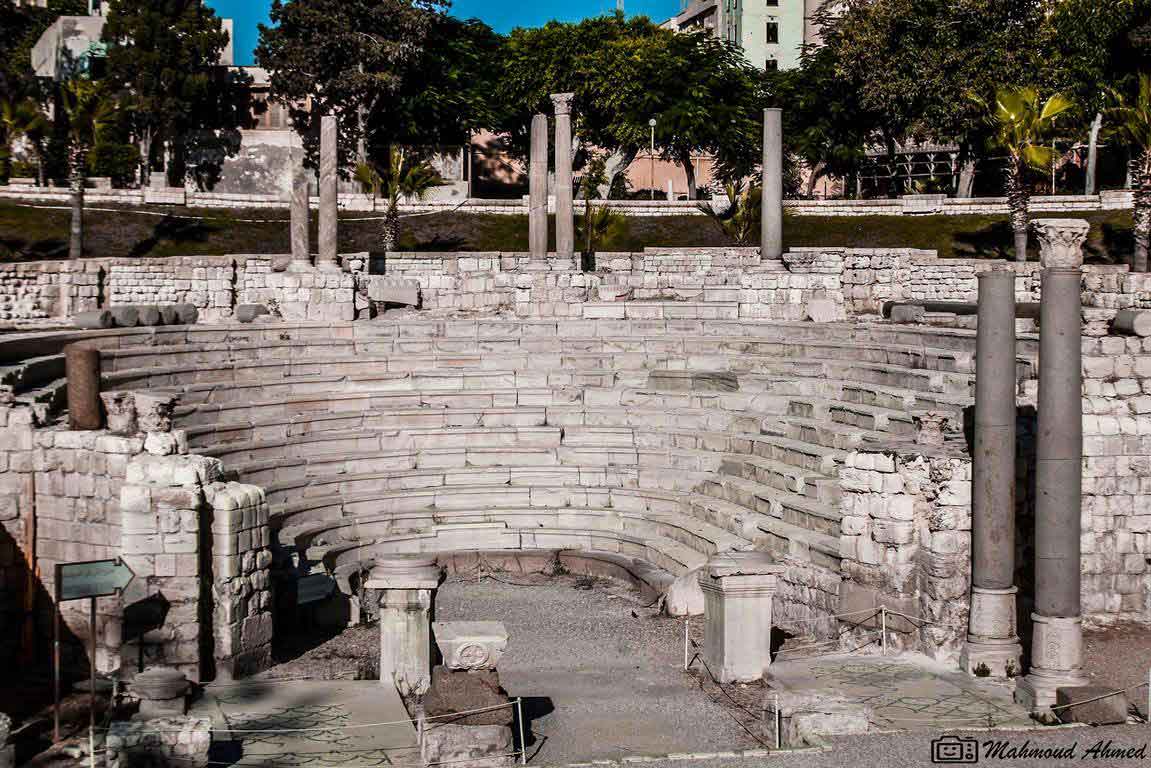
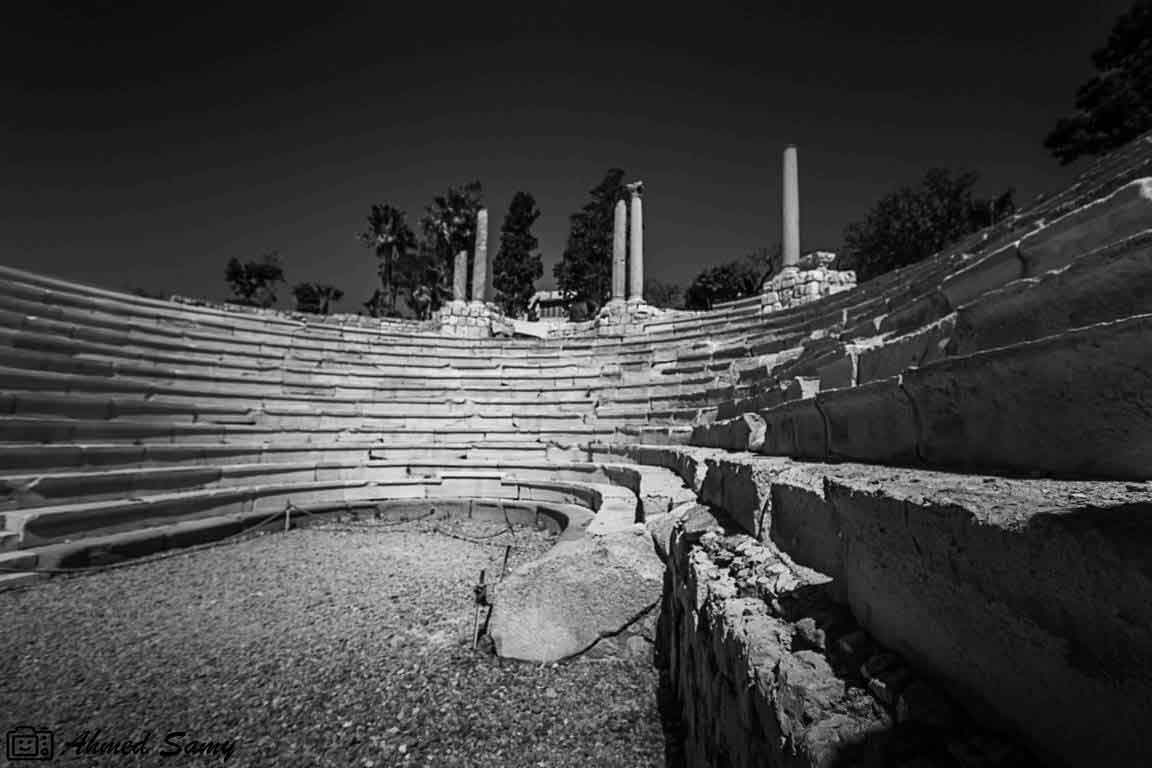
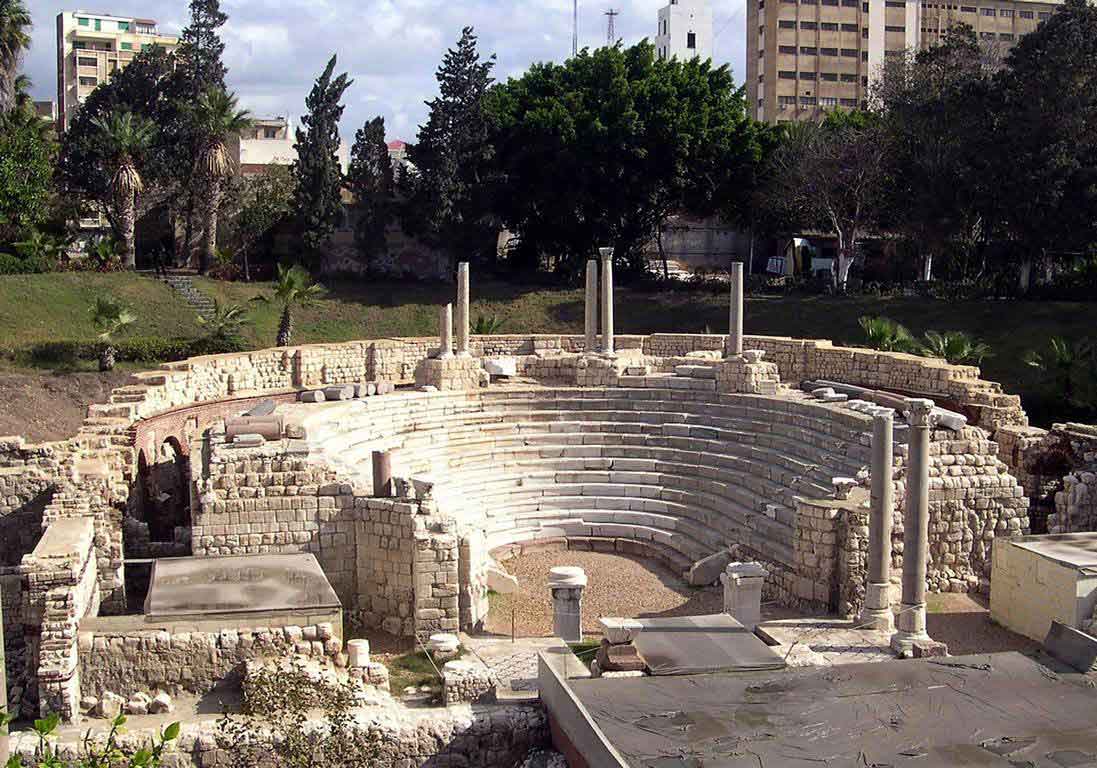
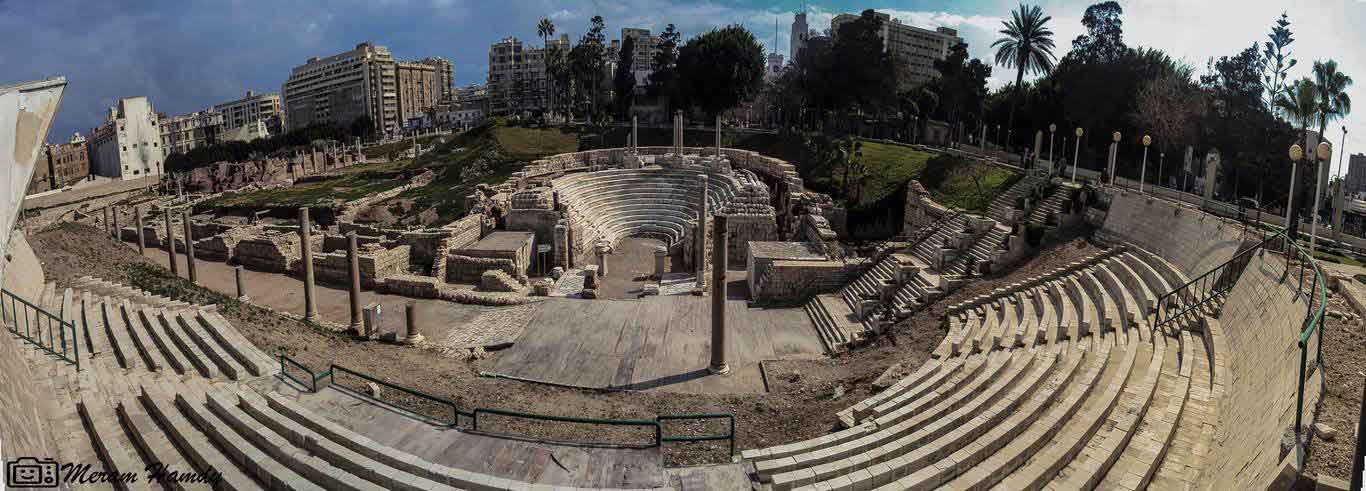
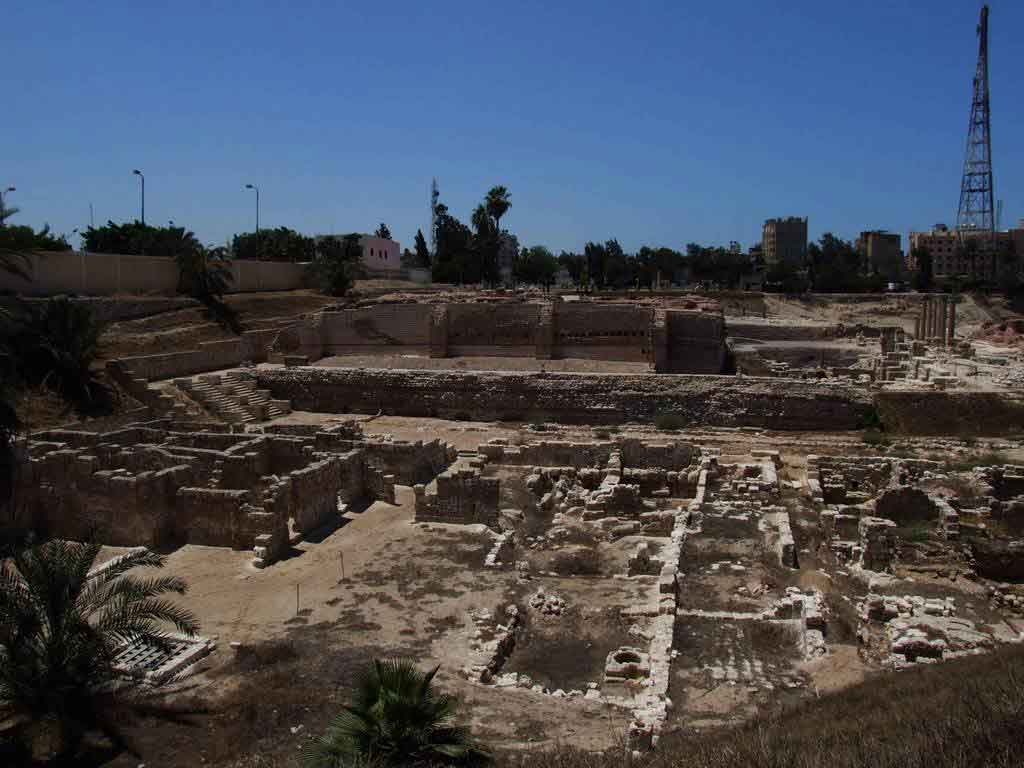
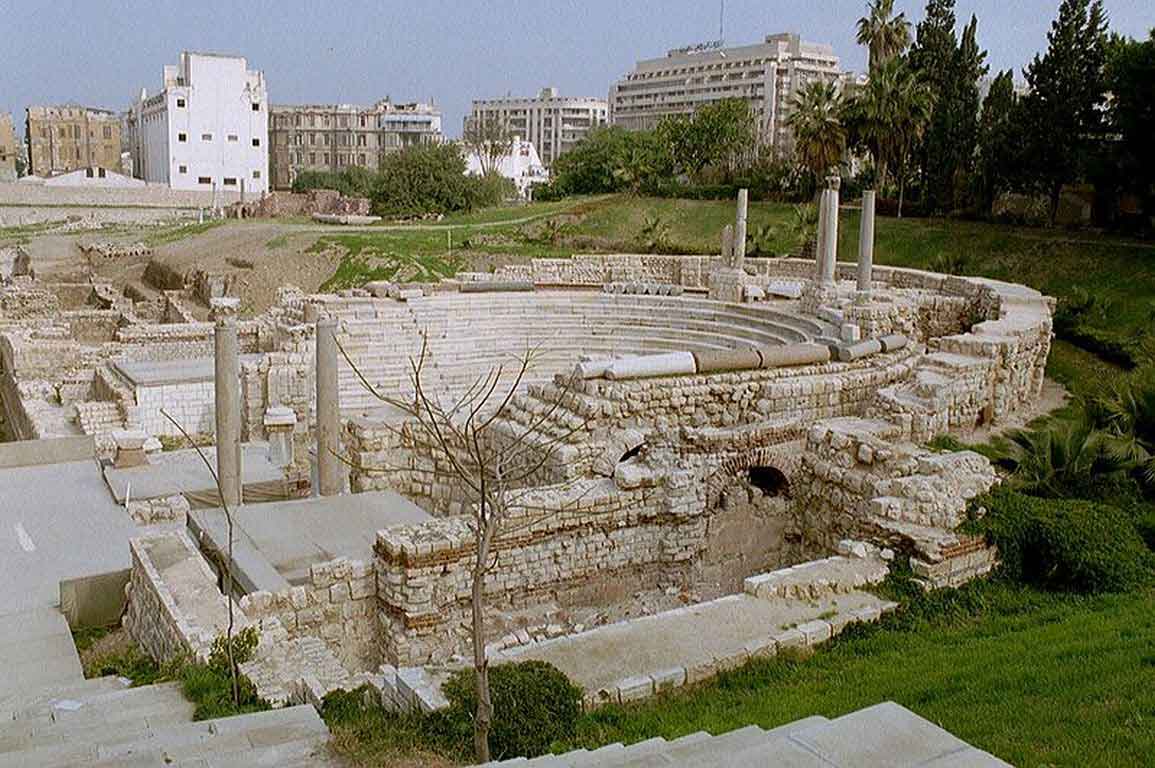
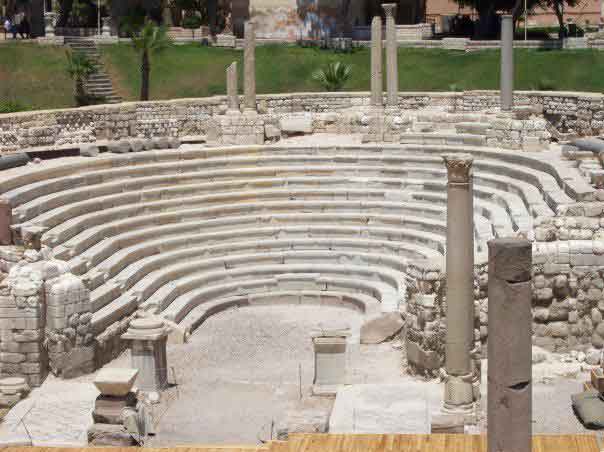
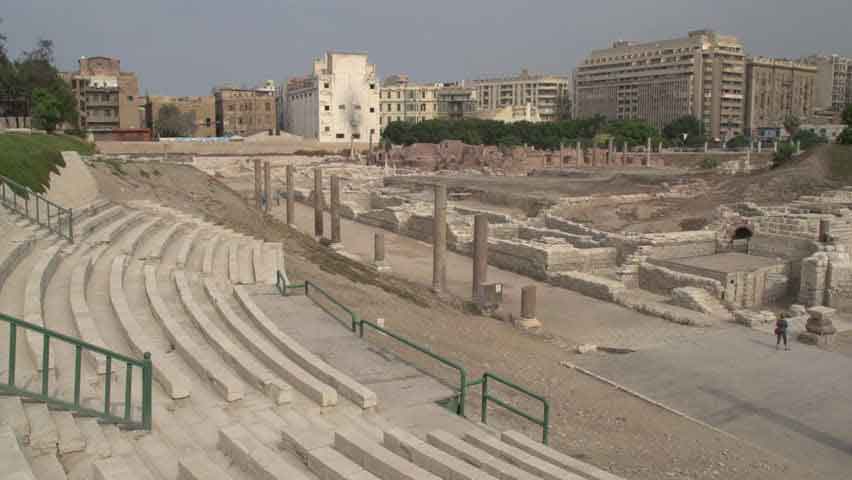
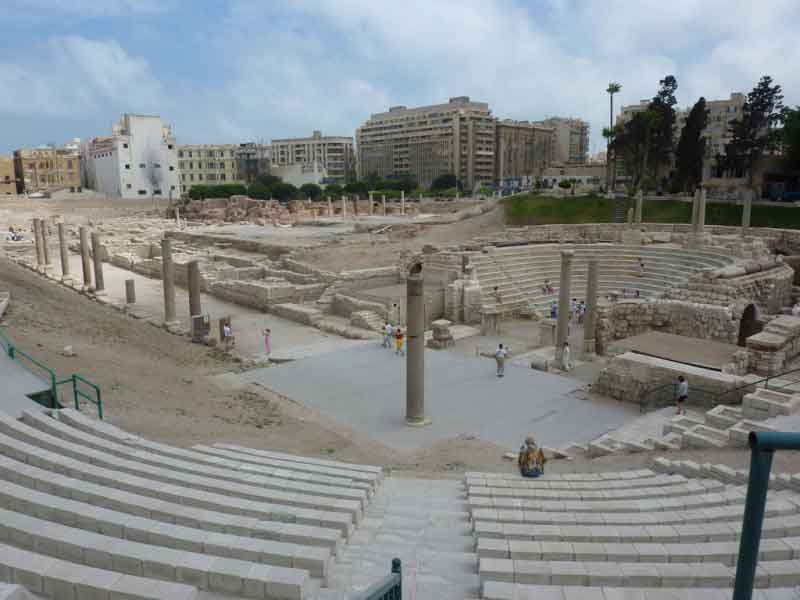






















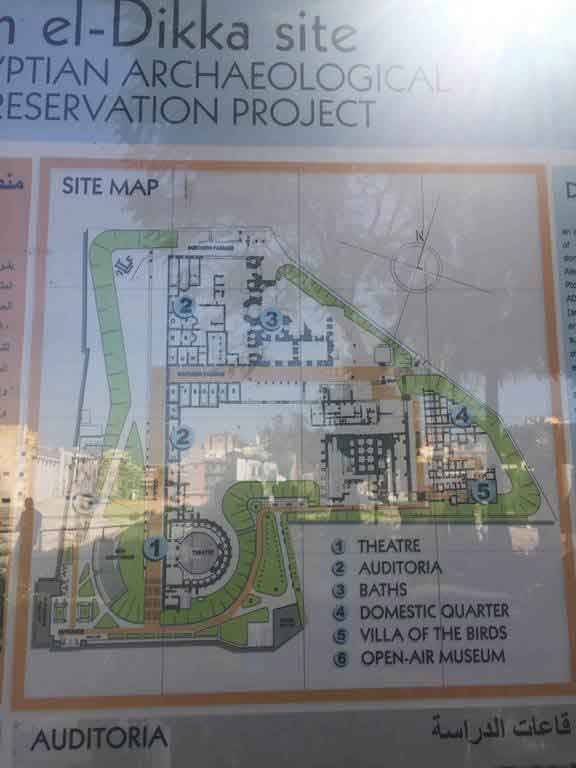





















The eastern part was chosen to be the Alexandria Museum and the southern part to be a Government complex. About 40,000 cubic meters of debris due to excavation have also been raised. The most important sights of the area are the Theater Road, which is 186 meters long from the north to the south. Next to the Roman amphitheater was also found a Roman tank, a Roman bath and a neighborhood whose buildings date from the first century AD till the Byzantine period, with the most famous villa "bird" and the end of the third or fourth century AD, the area was transformed into a public service represented by the area in the Roman, Roman baths and tanks besides the Byzantine University represented in the classrooms and when they began beating the foundations of the building they discovered red east and the Roman amphitheater was revealed.
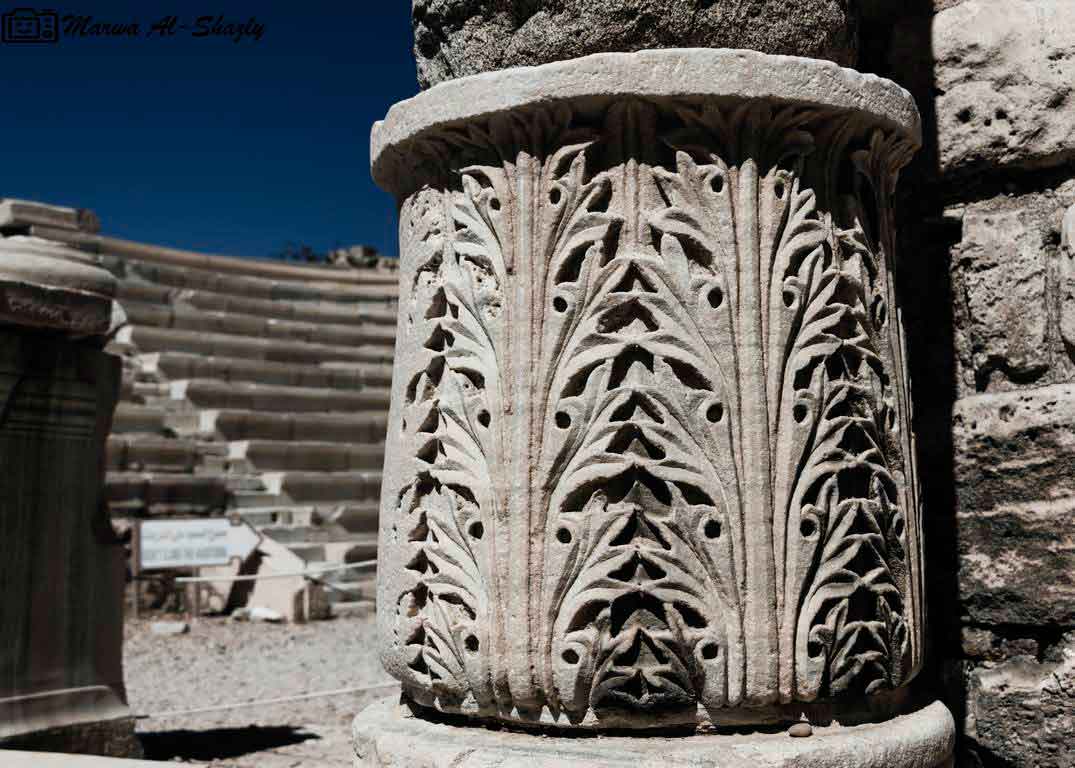
It is the only circular monument in Egypt along with the recent discovery of the Bluzium amphitheater in Sinai. Kom El-Dekka belongs to the Roman era of the beginning of the fourth century AD. It was in use until the Islamic era. at the beginning it had 16 rows in the Roman era and 2 entrances from the north and south and some pieces of marble seats and other architectural pieces that had been used in other buildings and were covered with a large red brick dome based on two large pillars in front, the corridor takes the shape of a U-shaped horseshoe and was used as a listening room in the Roman era and then reduced to 13 rows and seats for the first class and a set of marble and granite columns were added. of Byzantine-era colors, such as the corridor used as a town hall or a hall for political meetings after the earthquake of 535 AD, inscribed marble seats in addition to the first row of red granite have been found in one of the Greek inscriptions for the good fortune of winning the party which is evidence of the use of political meetings in the corridor in the Byzantine era. The interior wall of the building is of limestone and red stone, the exterior of limestone and red brick in some places, the orchestra was paved with marble in the past and at the two ends of two marble pillars one inscription in Arabic with a tribute 8th century, and recent statements by the Polish mission say that it was used as a large classroom.
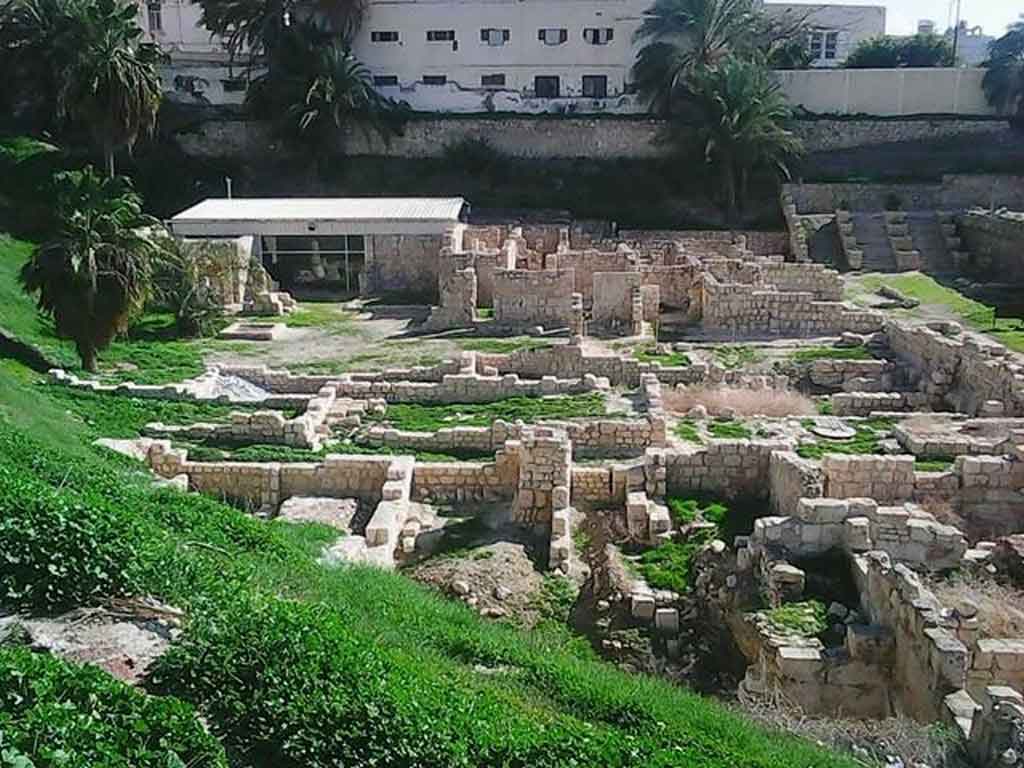
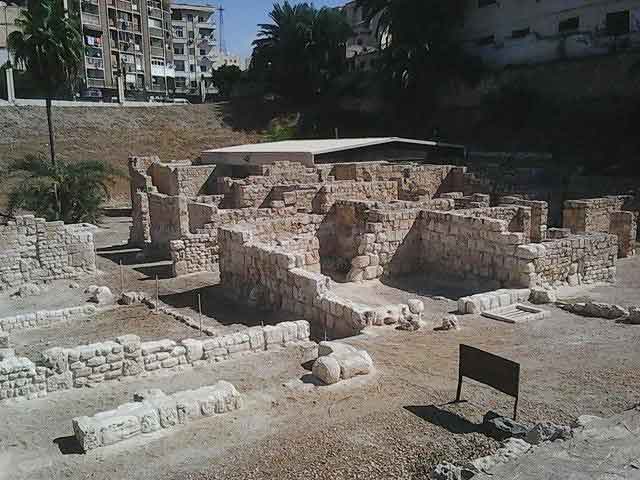
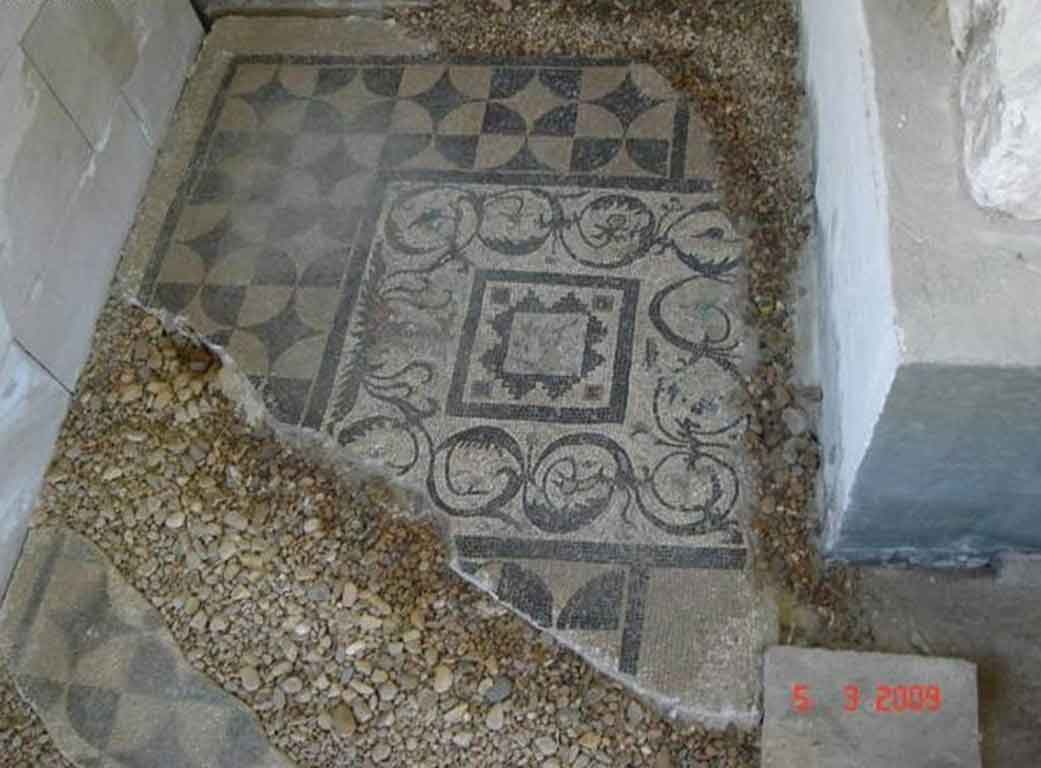
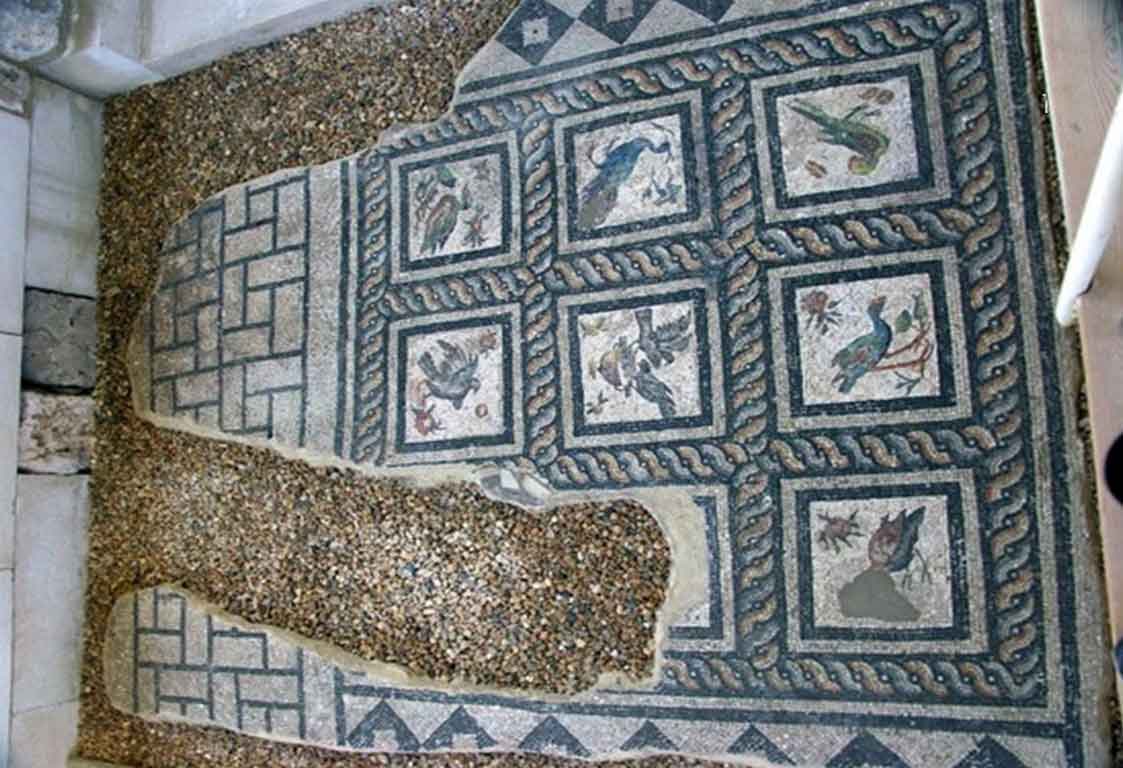
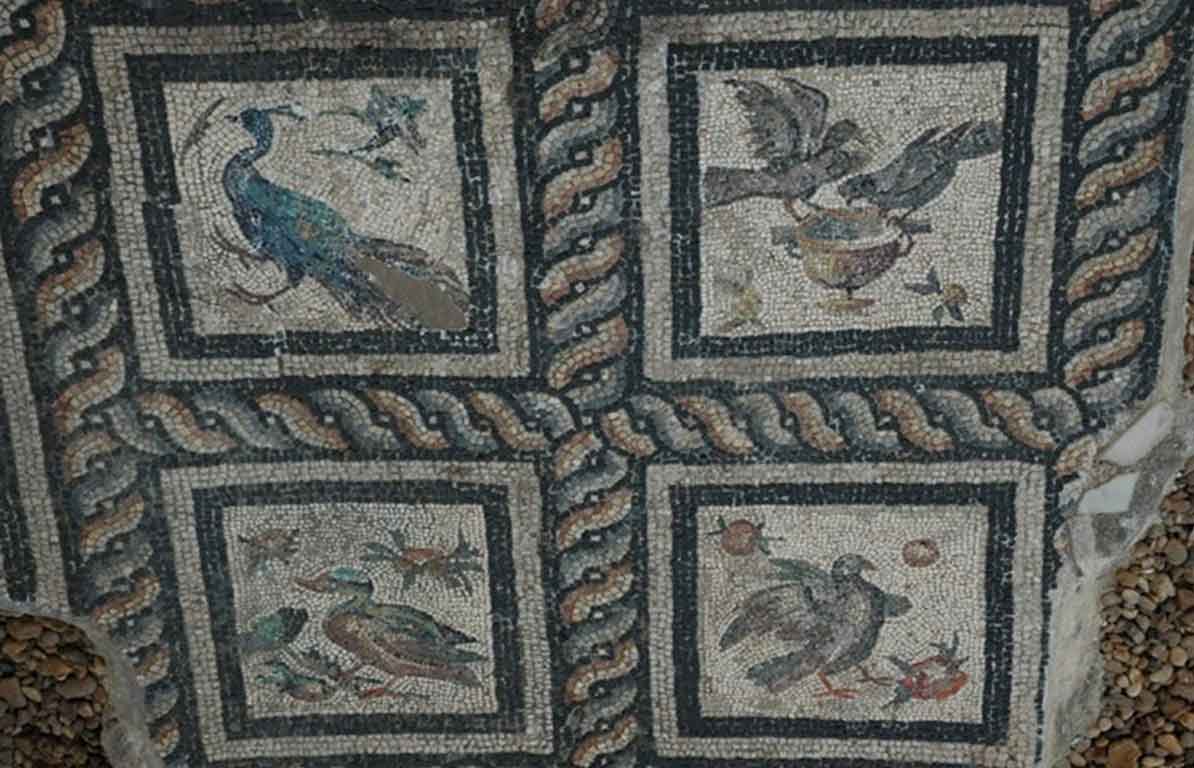
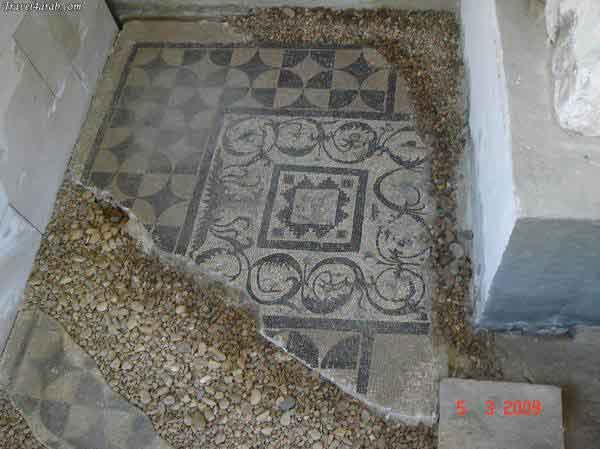
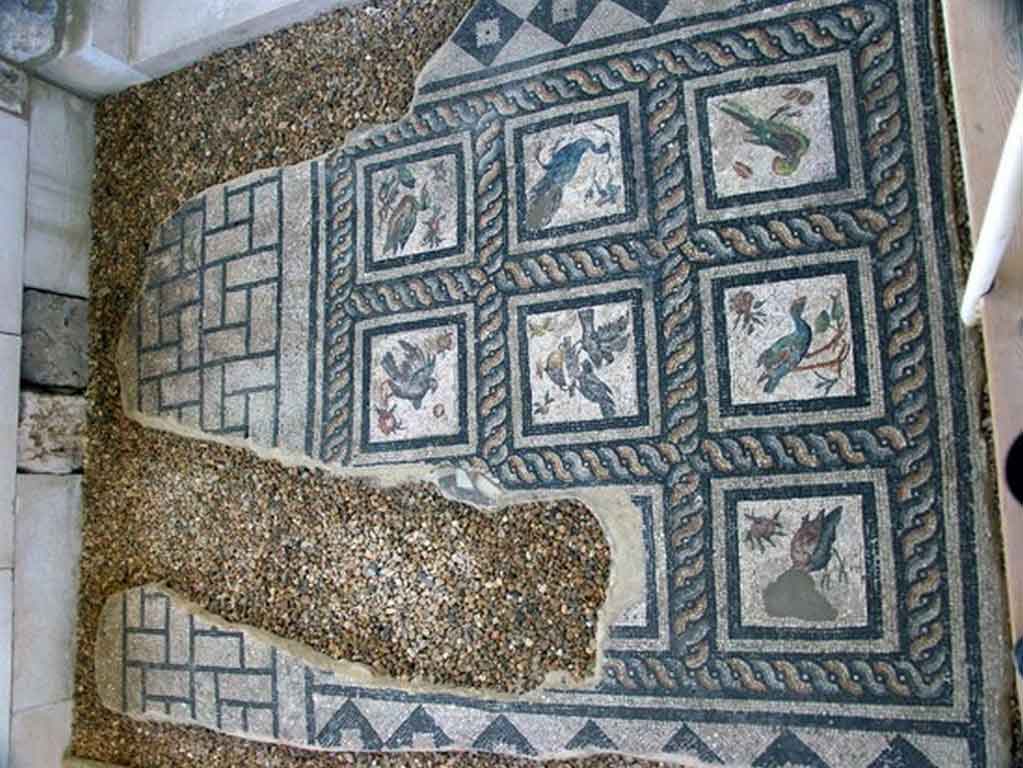
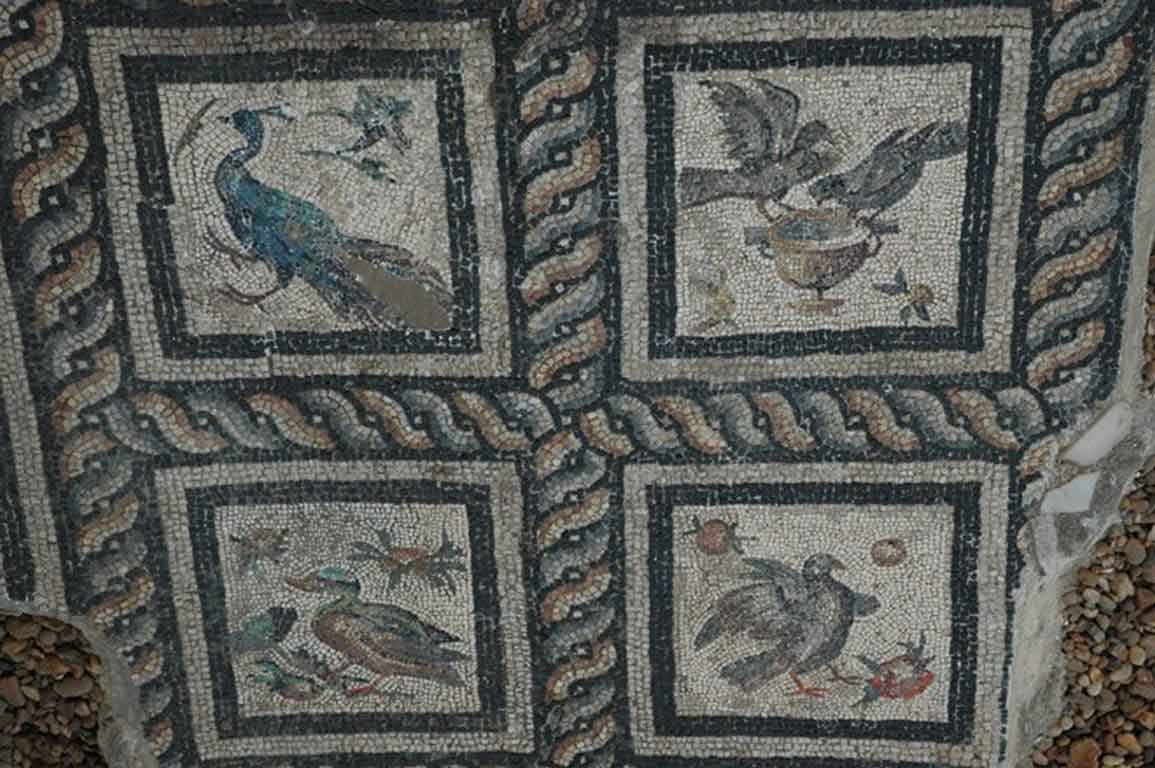
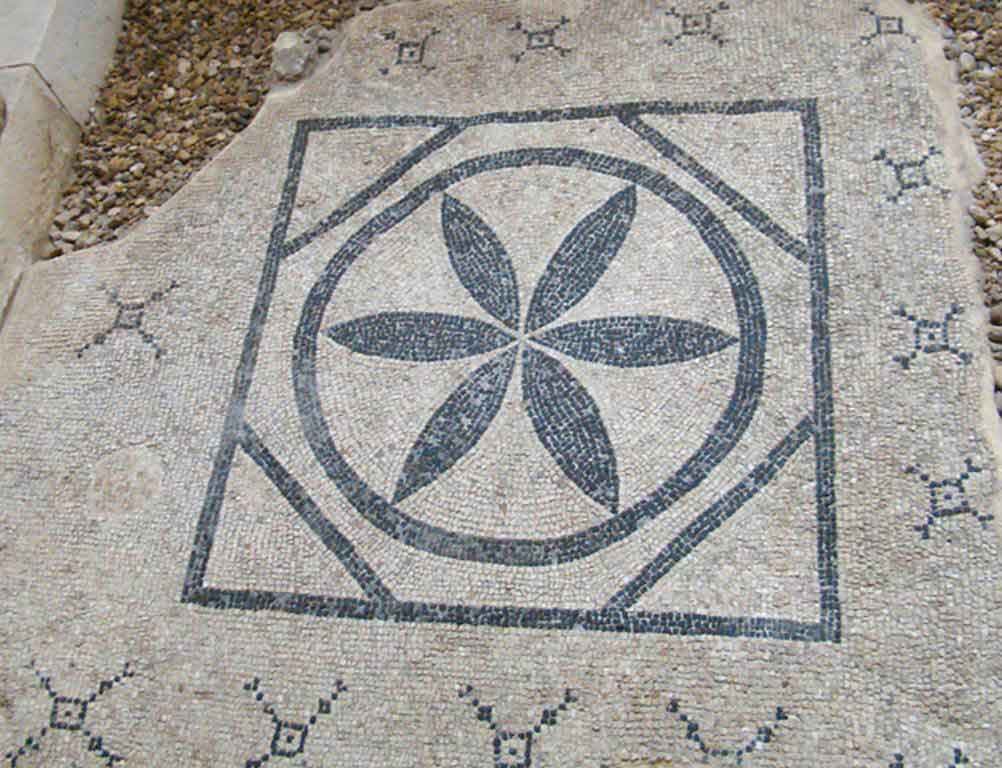
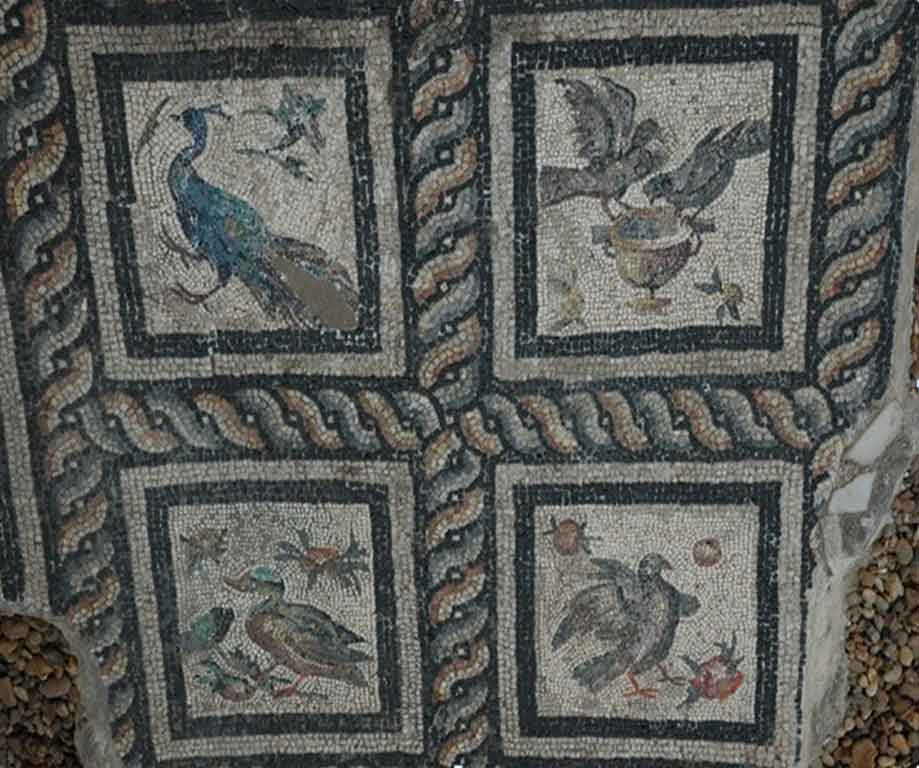
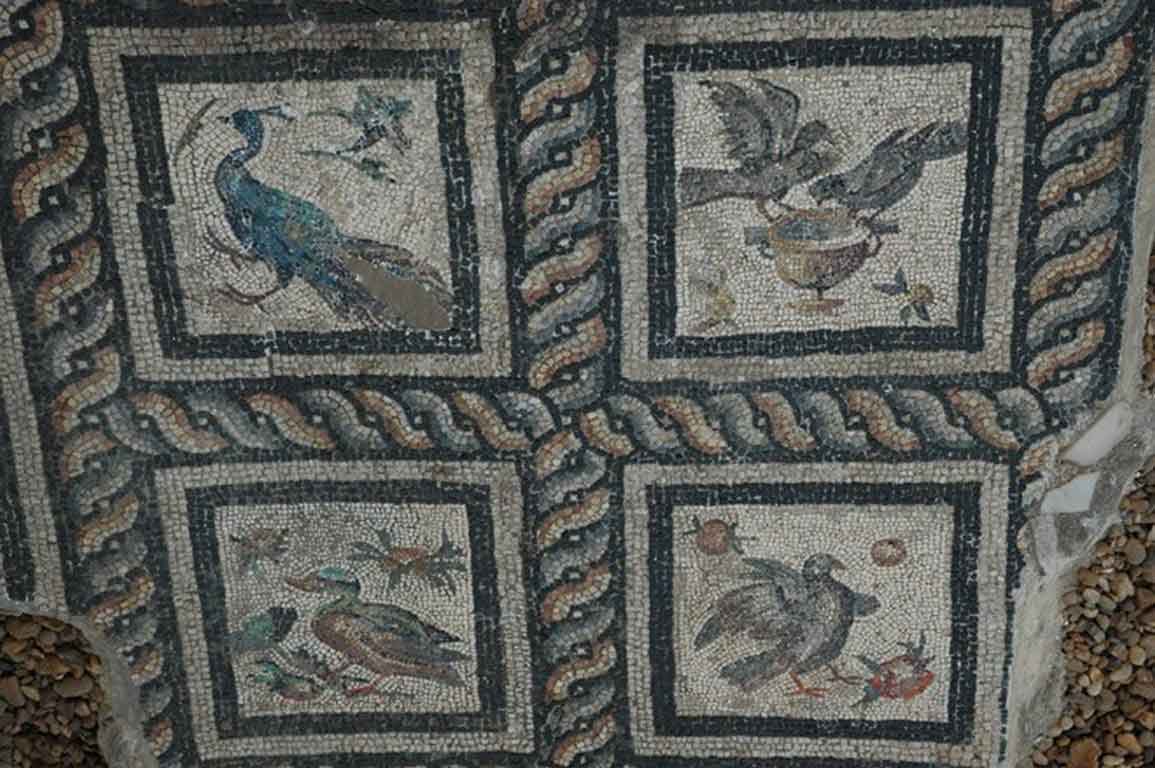
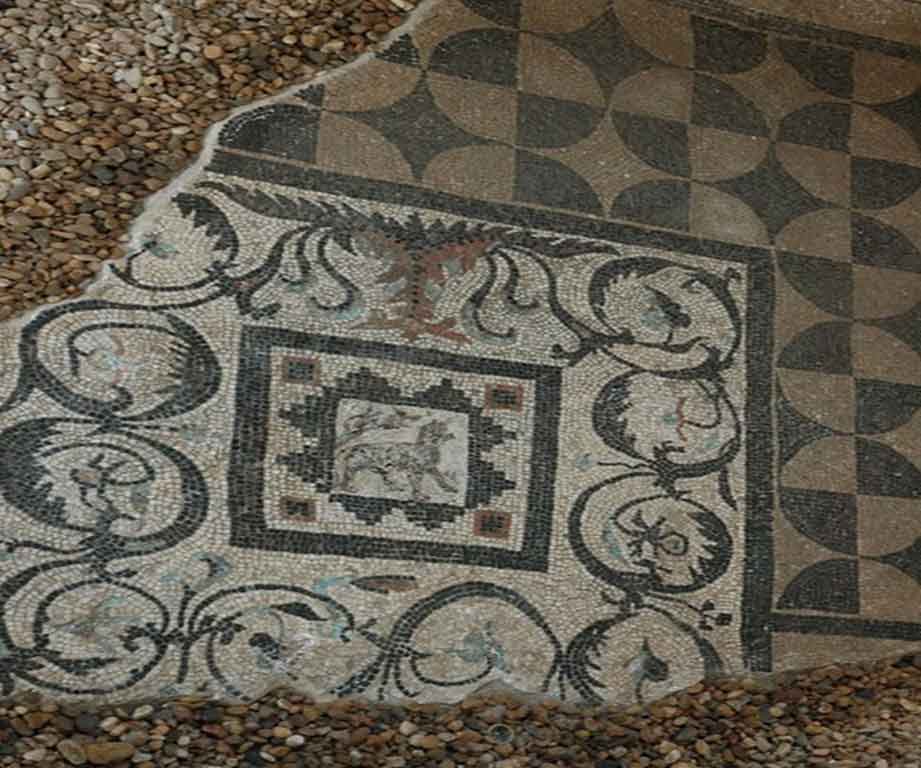
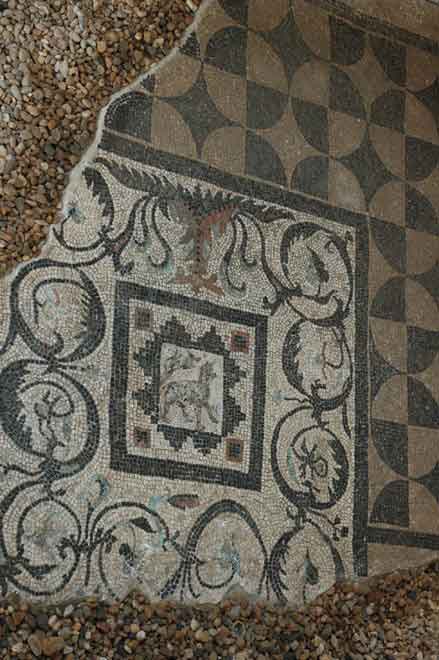
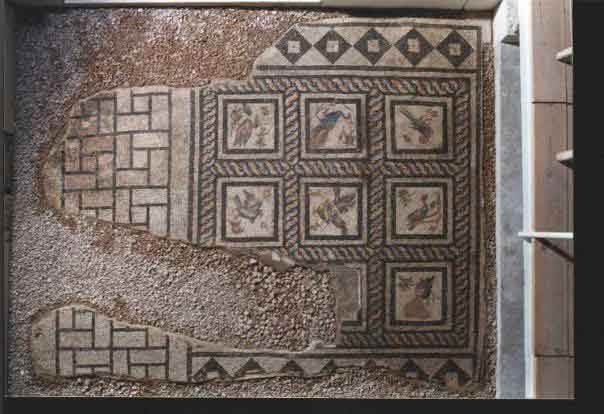
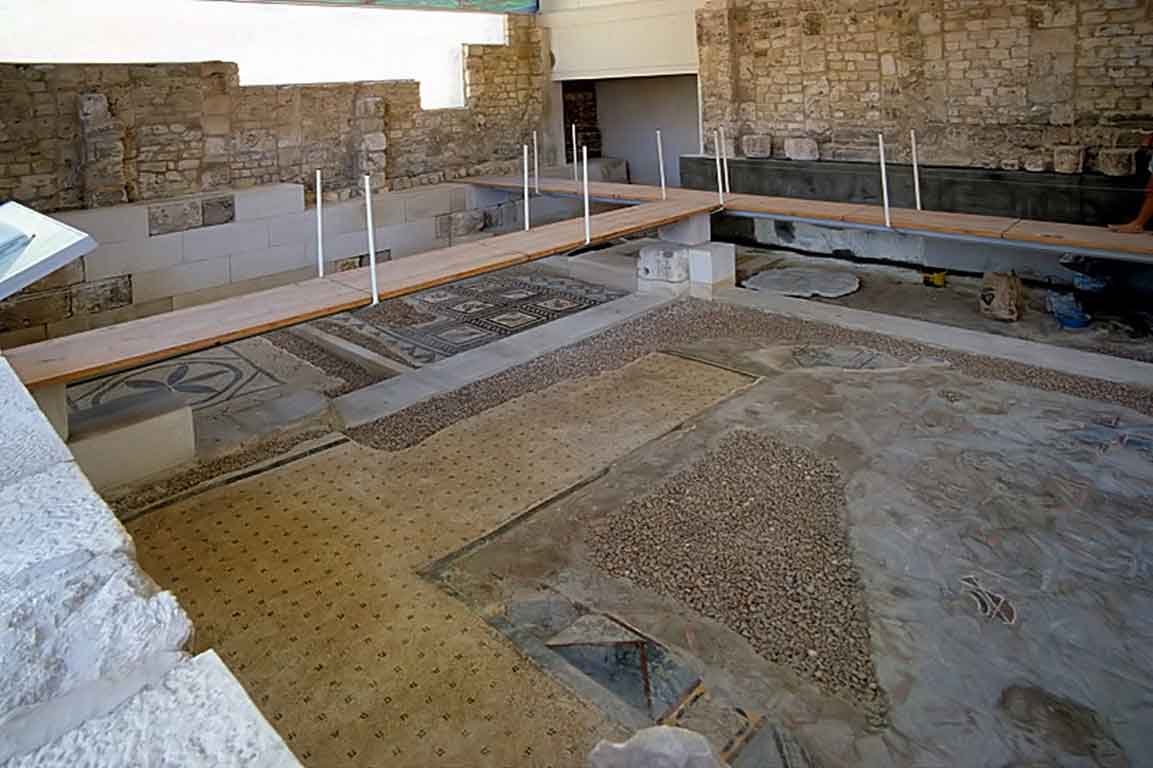
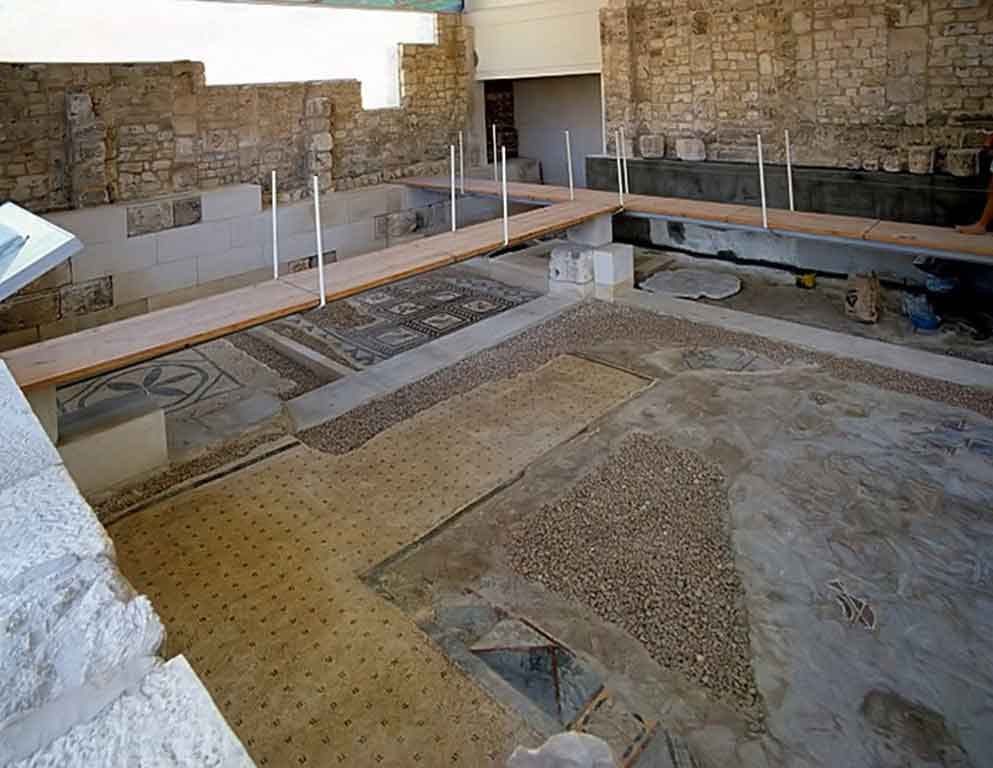
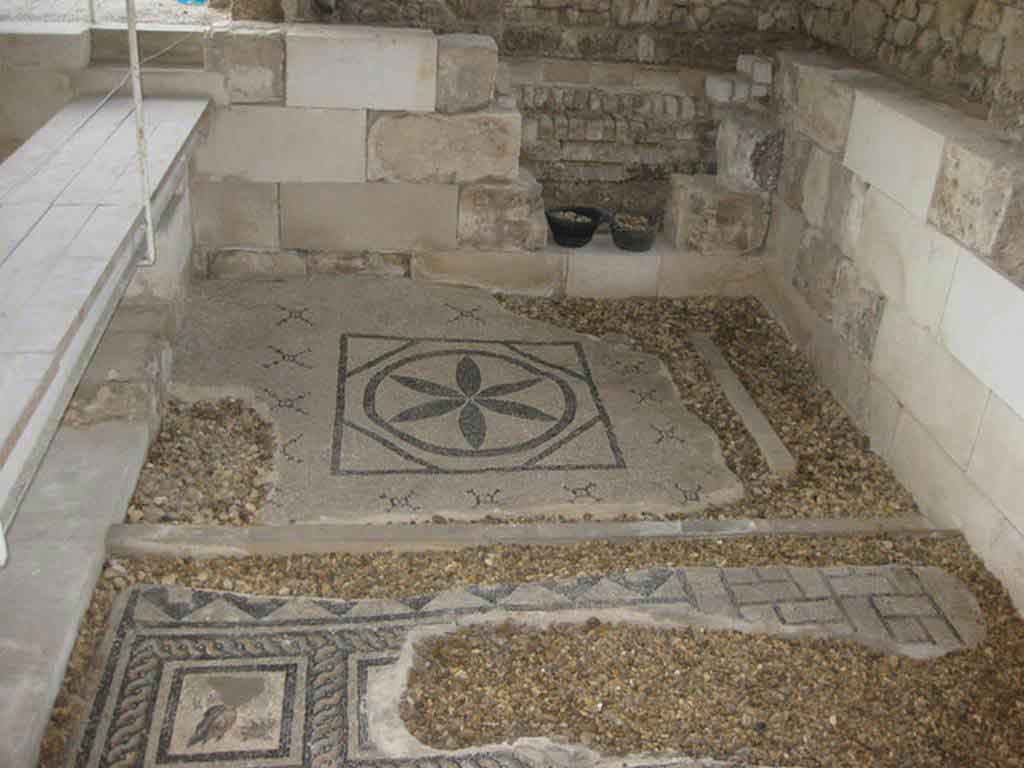
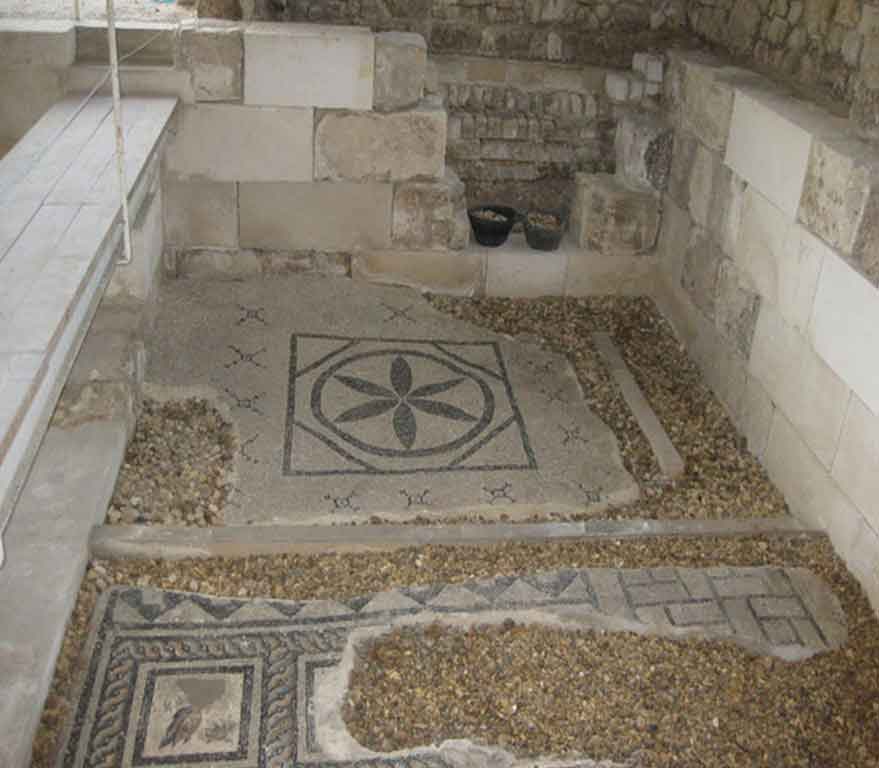
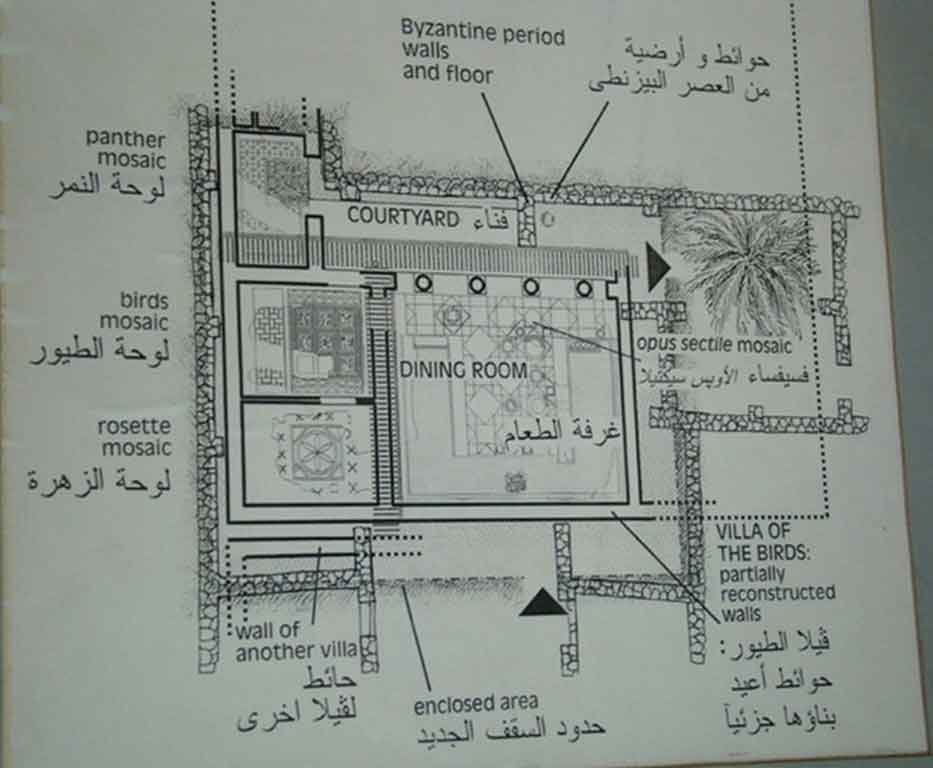
It is located in a residential neighborhood in the area. The Supreme Council of Antiquities and the US Research Center in Egypt have restored and protected the mosaic of the villa and the current area, which is about a quarter of the original site after the excavation, the entrance is still buried on the south side and the bathroom on the east side. The rest of the excavated rooms include the villa's courtyard and one of the oldest has a mosaic painting depicting a tiger's shape when displayed in a small square in the middle, and small stones, marble, glass and broken porcelain were used. 100 years AD, we can see the same technique in rossette flower painting dating back to 133 AD in relation to the coins found beneath the surface of the bird's image which is the most important painting in b villa dating from the late 2nd century BC. Also shown are colored small cubes with 7 pictures of different birds in the ground divided into 3 parts. Found only 7 then is the dining room divided into 3 sections three sofas are placed and in the middle the table. It was not in good condition especially after the fire that destroyed the villa at the end of the 3rd century following the blockade imposed by Diocletian in 297 AD or during the Aurelian domination and after many years in 450 AD. Address: Suleyman has a road next to Abdel Moneim on the south and Railway Station and Fuent North and Nabi Daniel on the west and SafiaZaghloul on the east.
